Real-Time Vehicle Communication
CAN Protocol
CAN Protocol Decoder Schematic
Controller Area Network (CAN) is an automotive industry standard for communication between vehicle electronic control units (ECUs). Each
ECU is connected on a shared CAN bus that is able to transmit and receive messages from the network.
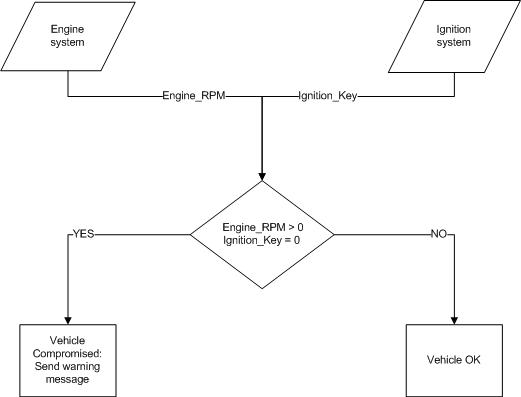
Specific CAN messages will be tracked to detect whether the vehicle has been compromised. CAN messages that are of interest are the Ignition system and Engine system. These systems are ECUs in the vehicle that are part of the CAN bus. By adding a CAN decoder device on the CAN bus which requests messages from the ignition and engine systems, the device will output warning to the BPSK Transmitter if the vehicle is compromised. CAN messages and decision processes used by the device are illustrated below.
ECU is connected on a shared CAN bus that is able to transmit and receive messages from the network.
Specific CAN messages will be tracked to detect whether the vehicle has been compromised. CAN messages that are of interest are the Ignition system and Engine system. These systems are ECUs in the vehicle that are part of the CAN bus. By adding a CAN decoder device on the CAN bus which requests messages from the ignition and engine systems, the device will output warning to the BPSK Transmitter if the vehicle is compromised. CAN messages and decision processes used by the device are illustrated below.
© Real-Time Vehicle Communication: RTVC Transmitter
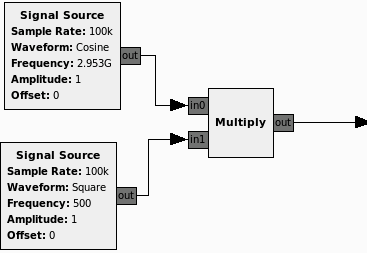
RTVC Package Transmitter contains a BPSK transmitter, which up converts the input square wave into an analog signal and transmits it using the vehicles antenna. The BPSK transmitter uses a center frequency of 2.953 GHz. This is because received signals require a receiver antenna to be 1/4 the length of the frequencies wavelength. So at 2.953 GHz, the receiver antenna will pick up the transmitted signal. The transmitter will provide a 43.95 dB gain, which will enable the RTVC receiver to pick up the transmitted signal up to the maximum range of 1.8 km. Figure 2 shows the design schematic for the transmitter.
BPSK Transmitter Schematic
BPSK Transmitter
 |
Create A Free Website With WebStarts.com |
